The Posterior Fossa Society is an international group of researchers and health care professionals doctors nurses psychologists speech pathologists linguists neuroscientists etc who are dedicated to research into the causes features treatment and prevention of the post-operative pediatric CMS and CCAS in children and adults. Posterior fossa syndrome is a collection of symptoms that can occur following surgical excision of a mass in the brain stem region.

Figure Anatomy Of The Brain The Pdq Cancer Information Summaries Ncbi Bookshelf
What is the indication for surgery.
. Since 1989 the two hospitals that comprise the setting for this study have treated 121 children with posterior fossa brain tumors. These effects are collectively known as Cerebellar Mutism Syndrome CMS or Posterior Fossa Syndrome. Posterior fossa arachnoid cysts are enclosed by the pia and arachnoid layers of the meninges and their contents have the same consistency as CSF.
A postoperative syndrome labeled posterior fossa syndrome has been identified in certain children. The symptoms generally occur as soon as 24 hours following surgery and can take as long as five days to appear. Most common posterior fossa primary brain tumor in adults.
These effects include loss of muscle tone memory troubles unsteadiness and decreased ability to talk. We observed that these PFACs can occur either in the midline within the fourth ventricle or retroclival region or extra-fourth ventricular region. Ritscher-Schinzel syndrome 1 Definition.
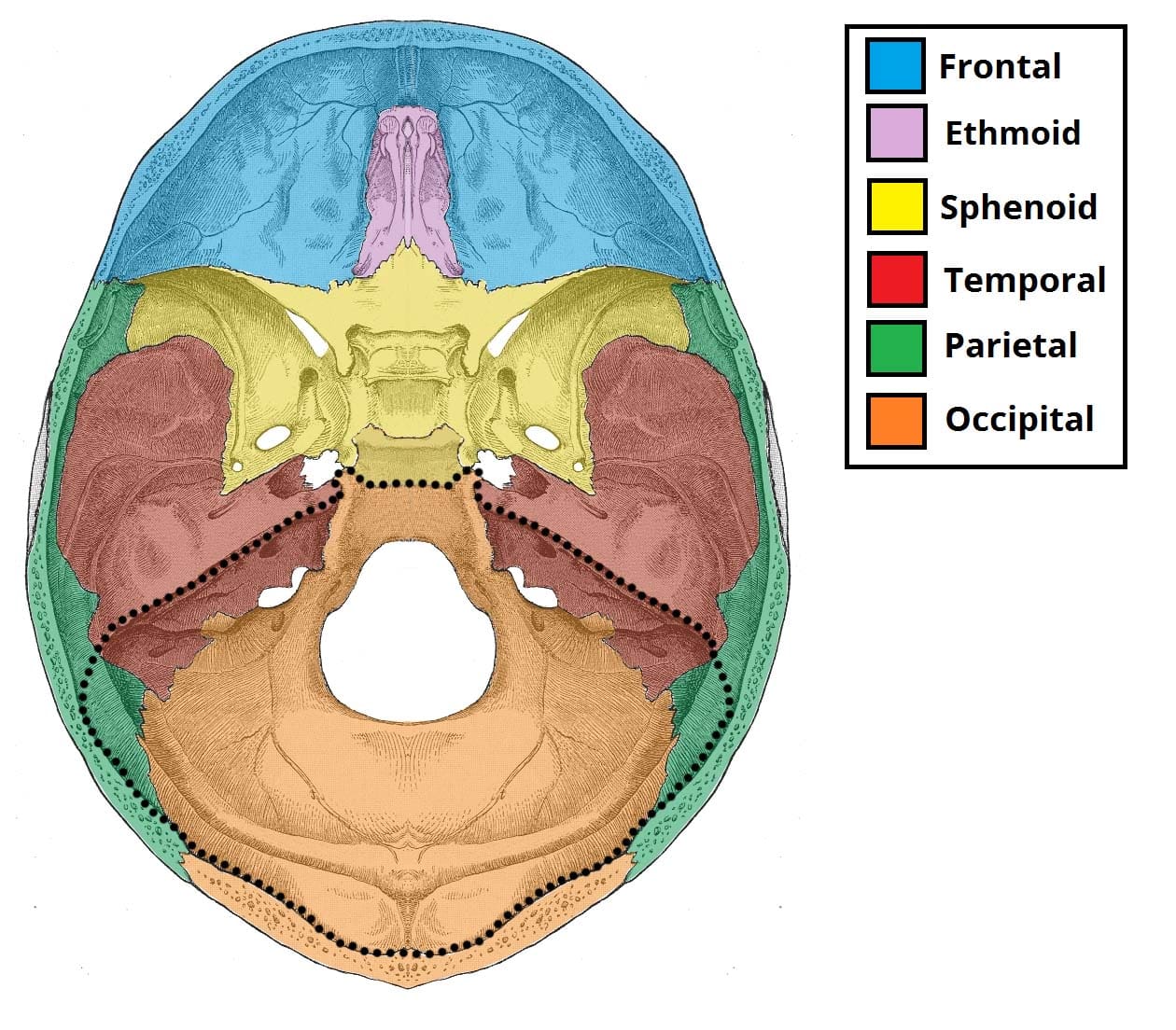
Its is formed by the sphenoid temporal and occipital bones. Approximately 60 to 70 of pediatric brain tumors originate in the posterior fossa. Especially lung cancer and breast cancer.
Posterior fossa meningiomas are tumors that form near the bottom of the skull by the brainstem and cerebellum. This is a large superior projection of bone that arises from the body of the sphenoid. It can also develop laterally in the CP angle or behind the cerebellum or as intracerebellar cyst.
The posterior cranial fossa Latin. 7 Symptoms typically begin with intermittent headache often worse in the morning followed by vomiting and eventually gait disturbance. The posterior cranial fossa is comprised of three bones.
They do not communicate with the fourth ventricle or with the subarachnoid space in the posterior fossa. If a tumor grows in the area of the posterior fossa it can block the flow of spinal fluid and. Purpose Posterior fossa tumors PFTs are the most common type of brain tumor in children.
Dysphagia is a known complication of PFT resection in children but data regarding risk factors and. Surgery in the areas to the rear of the skull also known as the posterior fossa or cerebellum can cause long lasting negative effects in children. Posterior fossa - axial CT image at level of pons Hover onoff image to showhide findings.
Children with posterior fossa syndrome usually have a collection of symptoms. Preoperative Evaluation and Questions. It is bounded as follows.
Within this fossa are two critical brain areas. The cerebellum is the part of the brain responsible for balance and coordinated movements. Craniotomy Posterior Fossa.
Posterior fossa tumor has a very different differential in an adult as opposed to a child. Although children lack expressive speech they may be able to process and understand information. Bones forming the posterior cranial fossa by Anatomy Next Borders of posterior cranial fossa.
Anteriorly and medially it is bounded by the dorsum sellae of the sphenoid bone. Posterior fossa tumors often cause hydrocephalus by blocking cerebrospinal CSF outflow pathways with resulting signs and symptoms of raised intracranial pressure ICP. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor very rare 5.
Superiorly the cerebellum is separated from the cerebral hemispheres by the tentorium cerebelli. This small area controls movement coordination and. These areas of the brain control the autonomic nervous system coordination and movement.
The brain stem and the cerebellum. The posterior fossa or posterior cranial fossa is the deepest and largest and is defined by the occipital bone of the skull. The posterior fossa is a small space in the skull found near the brainstem and cerebellum.
The most prominent symptom is limited or loss of speech. Posterior fossa syndrome tends to occur following surgery to remove a mass from the brain stem. The posterior fossa is a space near the base of the skull that contains the cerebellum and brain stem.
Masses in the cranial posterior fossa PF can cause a severe symptom burden due to vertigo cranial nerve palsy occlusive hydrocephalus or direct compression of structures within the brainstem10. Introduction Resection of brain metastases is an accepted therapeutic strategy for up to three large or symptomatic lesions. Posterior fossa Key points The posterior fossa accommodates the cerebellum and brain stem The posterior fossa accommodates the cerebellum and brain stem.
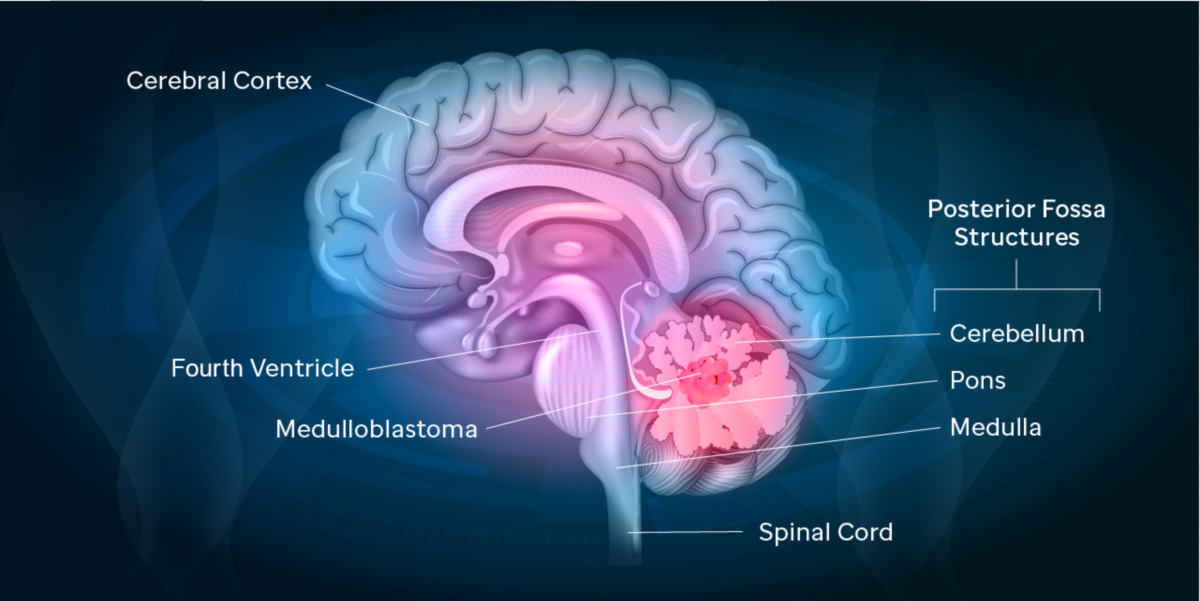
The posterior fossa is a small space in the skull found near the brainstem and cerebellum. Of the posterior fossa. Review of the behavioral and emotional aspects in pediatric cancer patients Abstract Medulloblastoma the most common malignant brain tumor of childhood occurs in the posterior fossa the part of the intracranial cavity that contains the brainstem and the cerebellum.
The brainstem is responsible for controlling vital body functions such as breathing. Some authors suggest that CM is only one symptom of the CMS complex that also includes ataxia. Hunt-Hess Grade for Aneurysm.
Also melanoma thyroid malignancies and renal cell cancer. Posterior fossa syndrome PFS or cerebellar mutism syndrome CMS is a collection of neurological symptoms that occur following surgical resection of a posterior fossa tumour and is characterised by either a reduction or an absence of speech. If a tumor grows in the area of the posterior fossa it can block the flow of spinal fluid and cause increased.
Cerebellar metastases most common. The cerebellum is the part of the brain responsible for balance and coordinated movements. The occipital bone and the two temporal bones.
Aneurysm AVM SAH Tumor Chiari Pre-op Neurologic condition. Ritscher-Schinzel syndrome RSS is a clinically recognizable condition that includes the cardinal findings of craniofacial feat. They are more commonly detected by routine prenatal ultrasound.
The brainstem is responsible for controlling vital body functions such as breathing. To investigate overcrowding in the posterior cranial fossa as the pathogenesis of adult-type Chiari malformation the authors studied the morphology of the brainstem and cerebellum within the posterior cranial fossa neural structures consisting of the midbrain pons cerebellum and medulla oblongata as well as the base of the skull while taking into. Fossa cranii posterior lies at the lowest level of the internal cranial base and is the largest of the three cranial fossae.
What Is Meaning Of The Posterior Fossa Is Unremarkable Quora

Getting To The Bottom Of A Medulloblastoma Mystery St Jude Progress
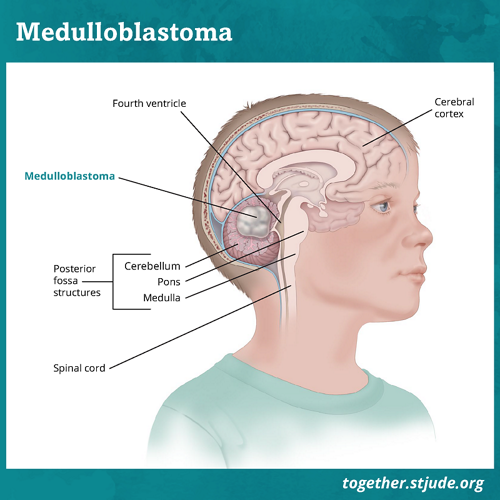
Posterior Fossa Syndrome Together

Posterior Cranial Fossa Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Posterior Cranial Fossa Wikipedia
Posterior Cranial Fossa Wikipedia
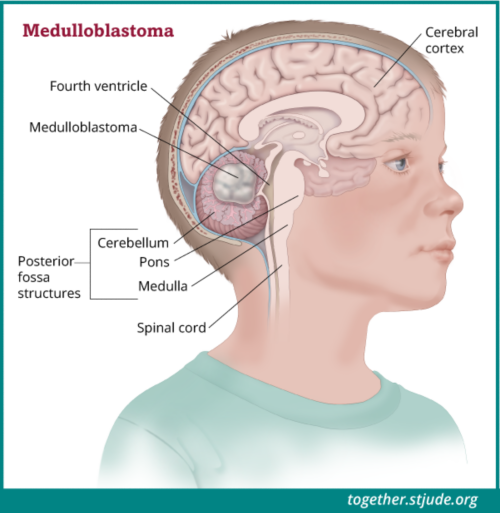
0 comments
Post a Comment